kDB
WARNING auKsys/5 has been released as stable, but this documentation has not been fully updated with changes since auKsys/4. In case of questions or mistakes, you can use the support project.
The Knowledge DataBase (kDB) is a library that provides functionnalities for storing knowledge, from low-level sensor data to high-level semantic information. kDB relies on PostgreSQL for storing the data. kDB provides API and tools for controlling and connecting to the server, storing and querying data.
Overview
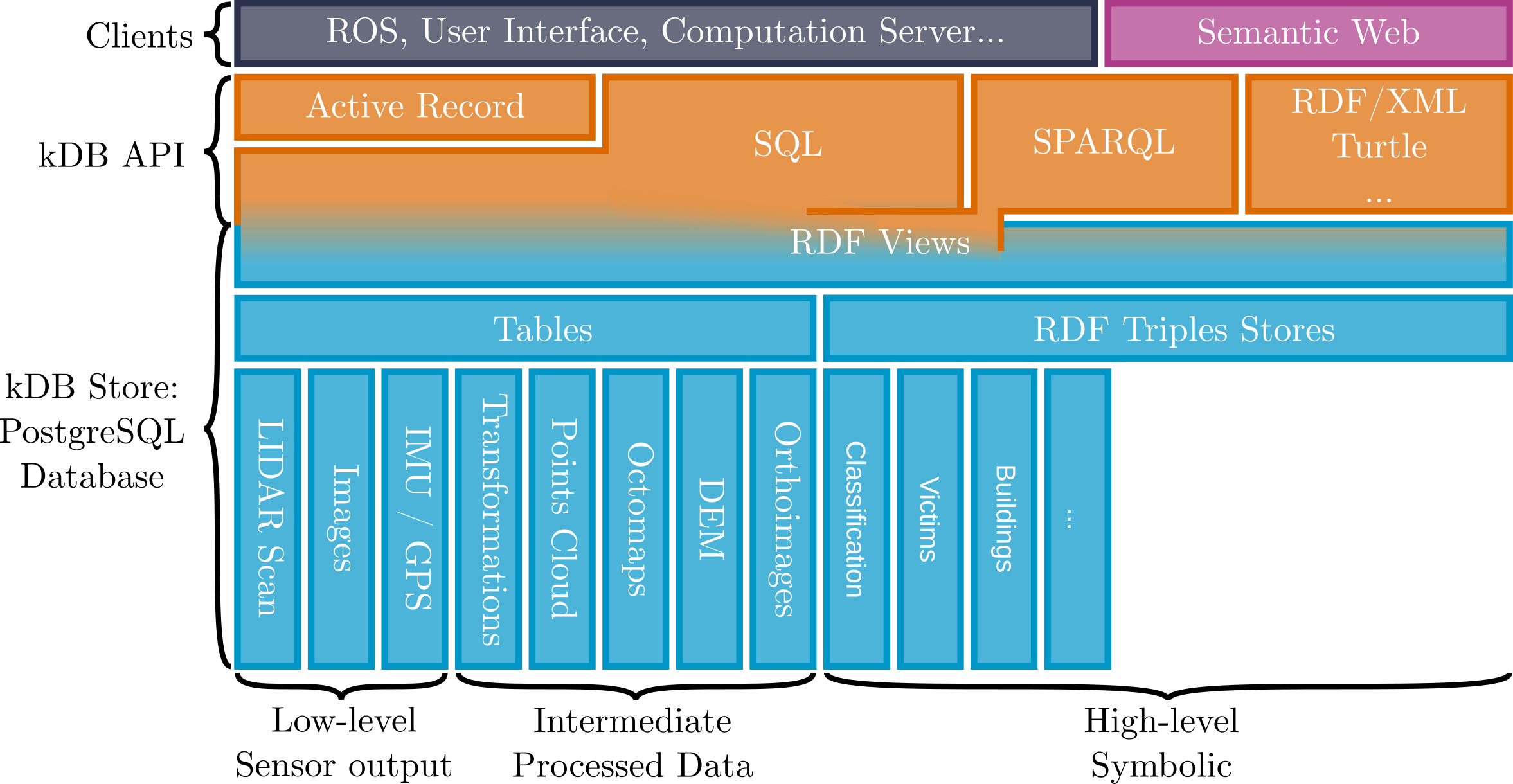
The figure below provides an overview of the library:
At the lowest level, data is stored in SQL Tables. kDB provides default schema for a number of type of data, it also allows to create custom tables by running custom SQL queries. kDB also provdides triples stores, that can be queries using SPARQL and where the data can be imported from RDF files.
The kDB API allows access to the data through different mechanism, using SQL or SPARQL queries, Active Records or RDF files. kDB also provides API for exchanging sensor data and automatic synchronisation of triple stores.
Clients are built on top of the API, several official clients are included in auKsys, such as the ROS server, an user interface (knowX), the computation server (pralin) and also an RDF compatible end-point.
Core Components
kDB/RDFDB: light weight implementation of a database, for RDF database.kDB/Repository: main library for interacting with a kDB Store.kDB/RDFView: implementation of (Sparqlify)[https://github.com/SmartDataAnalytics/Sparqlify] for mapping SQL tables to RDF Triples and querying with SPARQL.kDB/SPARQL
Extensions
kDBBaseKnowledgeallows to load base knowledge from a file system in the database.kDBDatasetssupport for storing datasets.kDBDataSynchronisationimplementation of the dataset exchange protocol.kDBDocumentsimplementation of a JSON-based document storage and query engine.kDBEndPointenables a SPARQL end-point.kDBPointCloudssupport for storing point cloud data in a kDB store.kDBQueriesgenerates API for querying the database with pre-defined SPARQL queries.kDBRDFGraphSynchronisationimplementation of th RDF Graph synchronisation protocol.kDBSensingsupport for storing sensor data in a kDB store.kDBGISsupport for storing GIS data in a kDB store.kDBMappingsupport related to storing 3d maps in a kDB StorekDBRoboticssupport for storing information related to robots in a database.
Qt/QML binding libraries and plugins:
kDBQuickkDBGISQuickkDBDatasetsQuick